Fatigue failure occurs due to crack propagation
Stage 1: Crack nucleation
Due to various flaws (inclusions, imperfections, voids) local stress concentration occurs. As a result local stress could exceed yielding stress and cause a slips along the boundaries. As a result micro crack appears
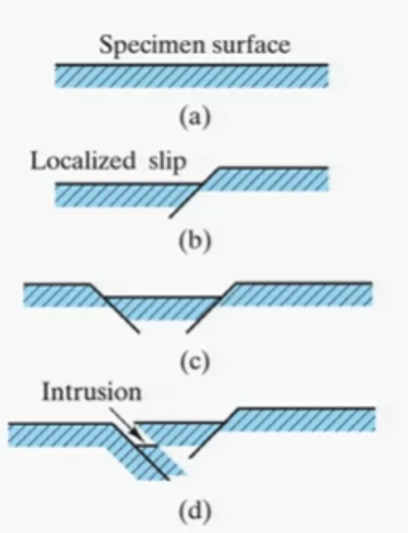
a) flaw-free surface
b) slip occurs due to different slip surfaces orientation
c) another slip near the first one
d) due to stress concentration more slips occurs and notch appears (crack on microscopic scale)
Stage 2: Crack propagation
During this stage crack grows slowly and orderly to some critical length
Stage 3: Unstable crack growth
When remain material couldn't carry applied load a rapid fracture happens.
Fatigue initiates at discontinuities
- change in cross-sectional area: keys, holes, other stress concentrations
- rolling/ sliding contact
- scratches, tool marks, assembly errors,
- material defects: voids, inclusions
Stress concentrations in Fatigue
Created: 13 July 2022
Last Update: 05 Sept 2022
Page last modified on September 26, 2022, at 07:37 PM
Powered by
PmWiki