References
Basics
Strength is inherent material property. It defines based on structure, processing and the treatment of the material. The main source of strength values are tests
Physical properties
Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (CTE) measures how the material will behave as temperature increases or decreases. It has units of 1/K or 1/C.
Strain due to thermal expansion is
\(\epsilon = \alpha\Delta T\)
| Material | CTE (*E-6, C^-1) |
| Aluminum | 23.6 |
| Copper | 17 |
| Gold | 14.2 |
| Iron | 11.8 |
| Tungsten | 4.5 |
| 316 Stainless Steel | 16 |
| 1025 Steel | 12 |
| Kovar | 5.1 |
| Alumina | 7.6 |
| Fused silica | 0.4 |
| Soda-lime glass | 9 |
| Silicon | 2.6 |
| Nylon 6.6 | 144 |
Units
| Type | Units |
| Imperial | lbf/in^2 = psi |
| Metric | N/m^2 = Pa |
| Soviet | kgs/mm^2 |
Stress-Strain diagram
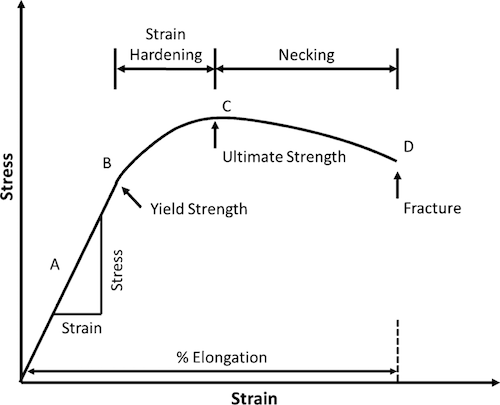
- yield strength (F_ty) is the maximum stress a material can endure beyond which it begins to permanently deform
- tensile strength (F_tu) is the maximum load that a material can support without fracture when being stretched
- Modulus of Elasticity (E) is a mechanical property that measures the tensile or compressive stiffness of a solid material when the force is applied lengthwise. It can be find as a slope of stress-straine curve in elastic region. Heat treatment has little impact on Elasticity Modulus
Typical values
| Material | Elastic Modulus |
| Rubber | 0.1 GPa (0.01 Mpsi) |
| ABS Plastic | 2.3 GPa (0.23 Mpsi) |
| Aluminum | 68 GPa (10 Mpsi) |
| Titanium | 110 GPa (16 Mpsi) |
| Carbon Steel | 200 GPa (29 Mpsi) |
Ashby Plots
For material selection, MF Ashby of Cambridge University developed a powerful method of material selection using charts and they're called Ashby plots.
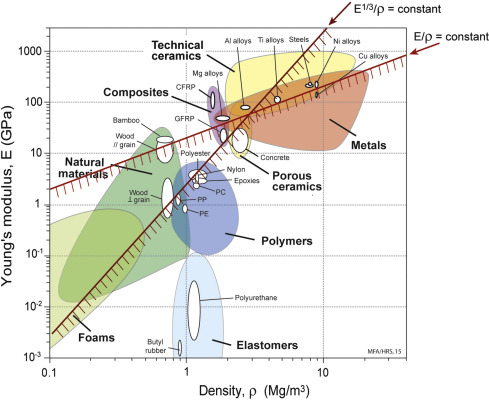
Using this chart engineer can get an idea which class of material he needs for a specific purpose.
Common Metals
Steel
Steel - iron alloyed with small percentage of carbon and other materials (chromium, manganese, etc)
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| high strength | heavy |
| high modulus of elasticity | |
| high hardness | |
| withstand high temperature |
Machinability, ductility and corrosion resistance could be controlled by adding alloyed elements.
In the US in steel name first two pair is composition, the next number pair - carbon content:
AISI 1040 Steel:
- 10 = Plain carbon
- 40 = 0.40% carbon
AISI 4340 Steel:
- 43 = Nickel-chromium-molybdenium
- 40 = 0.40% carbon
| Numbering | Composition |
| G10 | Plain carbon |
| G23 | Nickel |
| G31 | Nickel-chromium |
| G40 | Molybdenium |
| G41 | Chromium-molybdenium |
| G43 | Nickel-chromium-molybdenium |
| G46 | Nickel-molybdenium |
| G50 | Chromium |
| G51 | Chromium-vanadium |
Increasing in carbon content, increases strength but decreases ductility (elongation)
| AISI No | Processing | Yield strength, MPa | Elongation, % |
| 1010 | HR | 180 | 28 |
| 1010 | CD | 300 | 20 |
| 1045 | HR | 310 | 16 |
| 1045 | CD | 530 | 12 |
| 1095 | Q&T (425C) | 772 | 12 |
| 1095 | Q&T (650C) | 552 | 21 |
| 4340 | Q&T (425C) | 1360 | 10 |
| 4340 | Q&T (650C) | 855 | 19 |
Aluminum
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| strength to weight ratio | difficult to weld |
| corrosion resistant | not so strong |
| high thermal conductivity | |
| high electrical conductivity | |
| easy for machine, cast |
In the US in Aluminum name first letter is "A", first number is processing, the second number - main alloy group, the third number - modify/impurity limits, the last two - specify the minimum aluminum content between 99% and 100%.
UNS A96061 (or 6061):
- 9 = wrought
- 6 = magnesium and silikon alloying
- 0
- 61 = minimum aluminum content is 99.61%
| Numbering | Processing |
| 0 | cast |
| 9 | wrought |
| Numbering | Alloy group |
| 1 | Pure Aluminum |
| 2 | Copper |
| 3 | Manganese |
| 4 | Silicon |
| 5 | Magnesium |
| 6 | Magnesium and Silicon |
| 7 | Zinc |
Titanium
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| high temperature strength | expensive |
| good strength to weight ratio | difficult to machine |
| corrosion resistant | |
| bio compatible |
Heat treatment
Heat treating, these are time and temperature controlled processes
Quenching is when you heat the metal up to a high temperature and then you control the cooling rate. Typically, quenching is done quite rapidly. It increases the strength, the hardness, but it decreases the ductility and it can leave residual stresses in the material.
Tempering is when you heat the material up to below the critical temperature for the material and hold it there for a certain amount of time. What tempering does is it relieves residual stresses, it restores the ductility, but it reduces the strength.
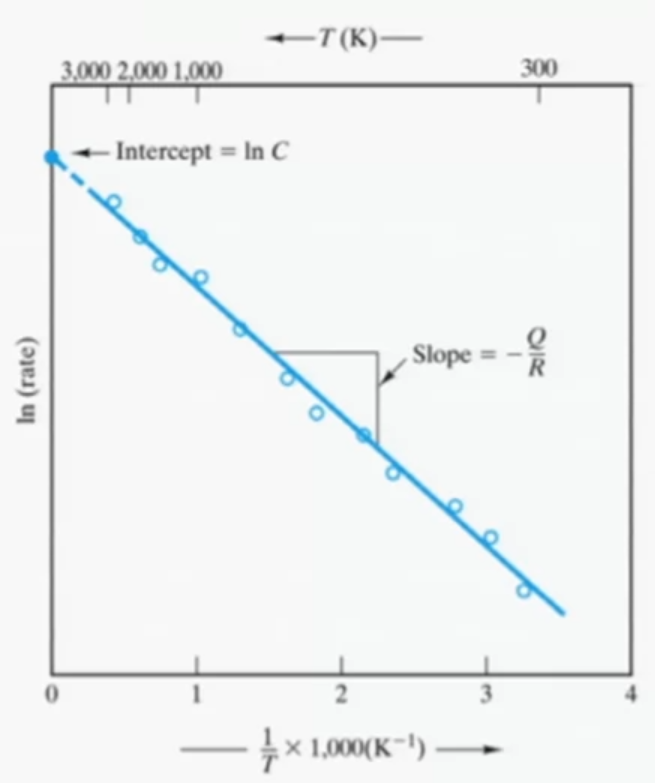
Arrhenius Relationship
Chemical reactions occur more rapidly as we go to higher temperatures and this relationship is exponential.
\(rate=Ce^{\frac{-Q}{RT}}\)
where:
- T = temperature
Rewriting it in linear form (y =b + mx) gives:
\(ln(rate)=ln(C)-\frac{Q}{R}\frac{1}{T}\)
For diffusion coefficient
\(D=D_0e^{\frac{-q}{kT}}\)
where:
- \(D_0\) - pre-exponential constant
- q - activation energy
- k - Boltzmann constant
- T = temperature, K