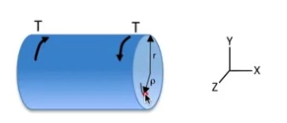
Torsional loading causes twisting deformations in rod.
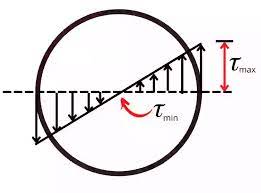
As a result, shear stresses appear in cross-section: \[\tau=\frac{T\rho}{J}\]
where:
- T - torque moment
- \(\rho\) - radial location
- J - polar moment of inertia (see Cross-section Properties)
According to the equation above, the most critical stress occurs at the extreme layers of bar
The angle of twist can be found by using: \[\varphi=\frac{TL}{GJ}\]
According to sign convention, positive stress at counter-clockwise direction of torque and negative - at clockwise direction of torque .
Page last modified on May 10, 2022, at 04:34 PM
Powered by
PmWiki