There are two kind of links in Linux
- Hard links
- Symbolic (soft links)
Hard links
Hard links are linked on file's inode pointing the real blocks with file on hard disk.
inode id could be found using ls -li command
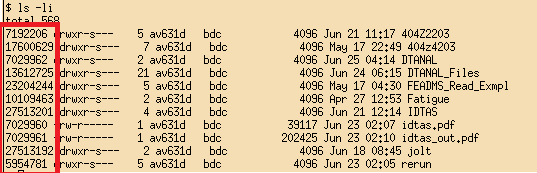
Limitations:
- Link should be on the same physical devise as the linked file
- Link could be on the file only. no directories allowed
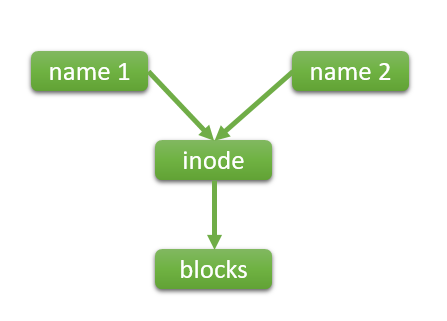
Different names could link to the same inode and they are equal in hierarchy. If one name removed, another will work. If file on risk changes it will reflect in both file names
To create hard link use the following command
ln file_name link_name
Example
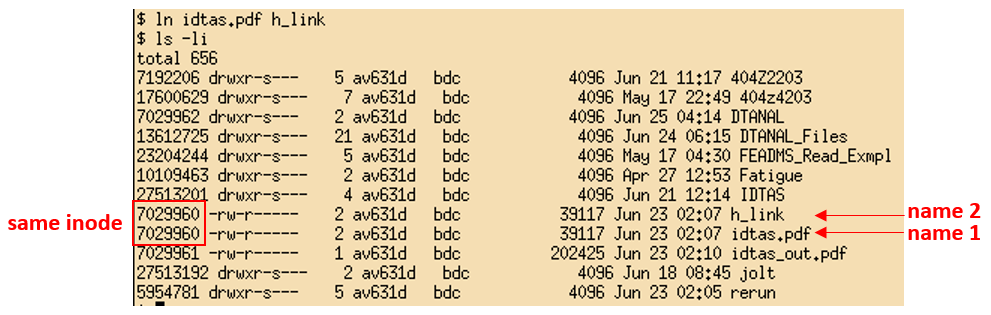
Symbolic links
Symbolic links connected to file name. If you remove file name symbolic link stop working
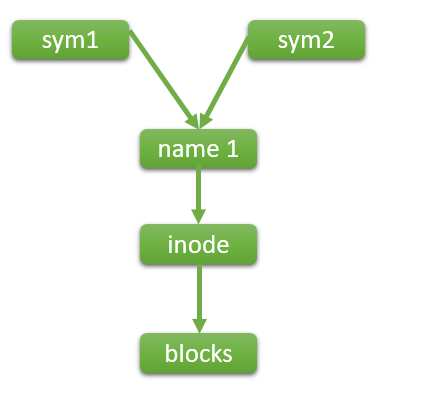
To create symbolic link use te folowing command To create hard link use the following command
ln -s file_name link_name
Example
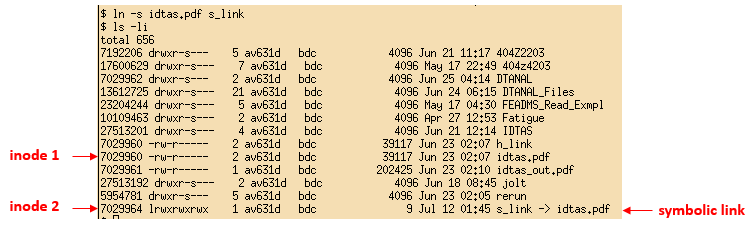
It's better to use absolute file name otherwise link will break after moving it to another folder
Page last modified on July 12, 2021, at 08:50 AM
Powered by
PmWiki